Create README.md
Browse files
README.md
ADDED
|
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1 |
+
# Pixel-aligned RGB-NIR Stereo Imaging and Dataset for Robot Vision
|
| 2 |
+
|
| 3 |
+
> **CVPR 2025**
|
| 4 |
+
> **Jinnyeong Kim**, **Seung-Hwan Baek**
|
| 5 |
+
> POSTECH
|
| 6 |
+
> [[arXiv]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.18025) • [[Code]](https://github.com/your-repo-url) • [[Video]](https://your-video-link.com) • [[Dataset on HuggingFace]](https://huggingface.co/datasets/your-dataset-url)
|
| 7 |
+
|
| 8 |
+
---
|
| 9 |
+
|
| 10 |
+
## Overview
|
| 11 |
+
|
| 12 |
+
This repository provides the code and dataset accompanying our CVPR 2025 paper:
|
| 13 |
+
|
| 14 |
+
**"Pixel-aligned RGB-NIR Stereo Imaging and Dataset for Robot Vision"**
|
| 15 |
+
|
| 16 |
+
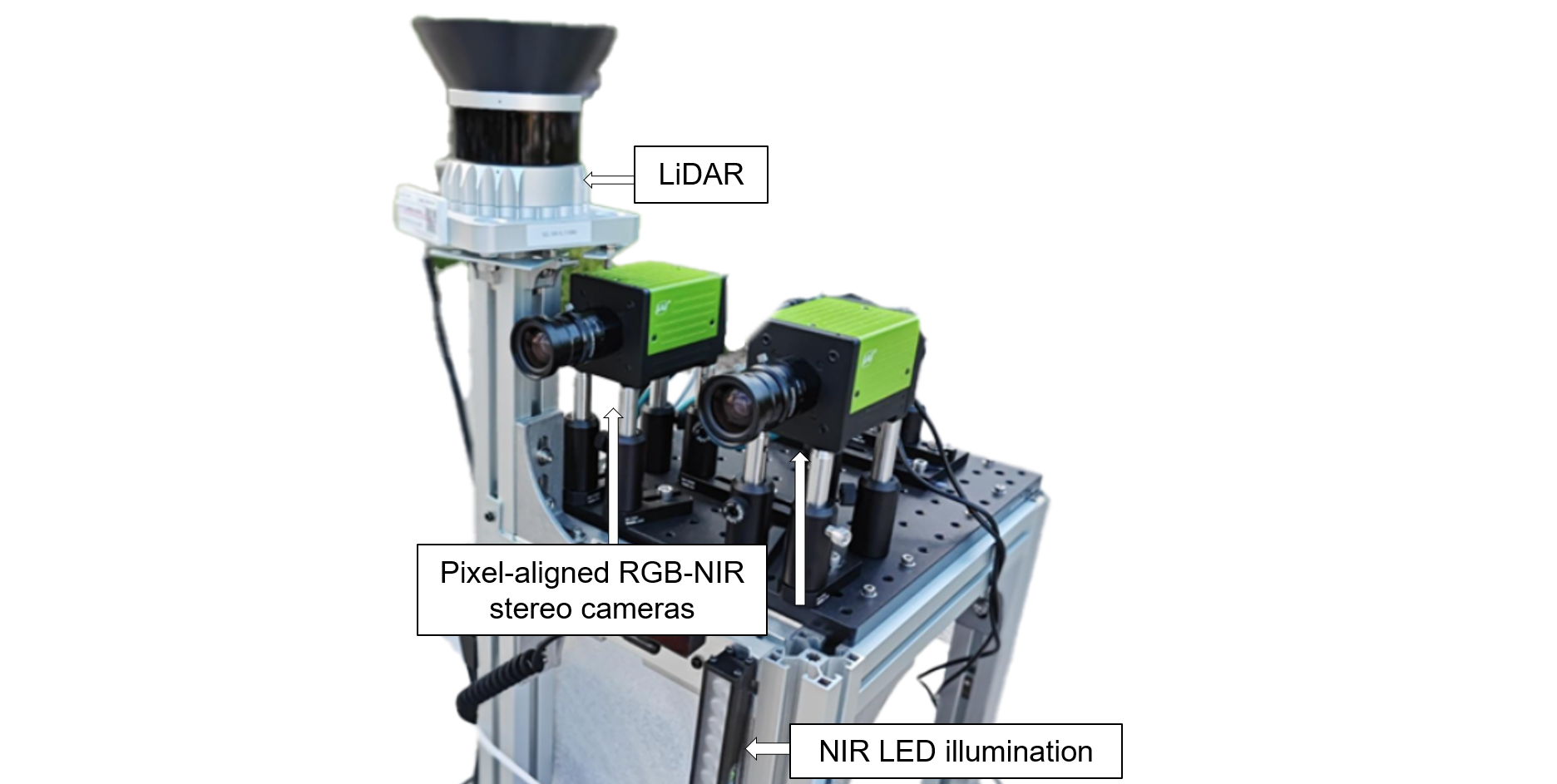
We propose a novel robotic vision system equipped with **two pixel-aligned RGB-NIR stereo cameras** and a **LiDAR sensor** mounted on a mobile robot. Our system captures **RGB-NIR stereo video sequences** and **temporally synchronized LiDAR point clouds**, offering a high-quality, aligned multi-spectral dataset under diverse lighting conditions.
|
| 17 |
+
|
| 18 |
+
|
| 19 |
+
|
| 20 |
+
---
|
| 21 |
+
|
| 22 |
+
## ✨ Highlights
|
| 23 |
+
|
| 24 |
+
- **Pixel-aligned RGB-NIR stereo imaging** for robust vision under challenging lighting.
|
| 25 |
+
- **Continuous video sequences** recorded using a mobile robot.
|
| 26 |
+
- **Sparse LiDAR point clouds** temporally synchronized with stereo imagery.
|
| 27 |
+
- Two proposed methods to utilize RGB-NIR pairs:
|
| 28 |
+
- RGB-NIR **Image Fusion** (pretrained model-compatible)
|
| 29 |
+
- RGB-NIR **Feature Fusion** (for fine-tuned stereo depth estimation)
|
| 30 |
+
|
| 31 |
+
---
|
| 32 |
+
|
| 33 |
+
## 📦 Dataset
|
| 34 |
+
|
| 35 |
+
We release a large-scale dataset for training and evaluating robot vision models in realistic environments.
|
| 36 |
+
|
| 37 |
+
### 📹 Data Statistics
|
| 38 |
+
|
| 39 |
+
| | #Videos | #Frames |
|
| 40 |
+
|---|--------|---------|
|
| 41 |
+
| Training | 80 | 90,000 |
|
| 42 |
+
| Testing | 40 | 7,000 |
|
| 43 |
+
|
| 44 |
+
### 📁 Per Frame Data Includes:
|
| 45 |
+
|
| 46 |
+
- Pixel-aligned **RGB-NIR stereo images**
|
| 47 |
+
- **Sparse LiDAR** point cloud (in camera coordinates)
|
| 48 |
+
- **Sensor timestamps** (synchronized)
|
| 49 |
+
|
| 50 |
+
### 🌗 Lighting Scenarios
|
| 51 |
+
<img width="920" alt="image" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/a07bea4e-5674-4277-a585-f556ce9d4825" />
|
| 52 |
+
|
| 53 |
+
|
| 54 |
+
➡️ **[Code is availabe on github](https://github.com/divisonofficer/Pixel_aligned_RGB_NIR_Stereo)**
|
| 55 |
+
|
| 56 |
+
Each .tar.gz file follows below structure
|
| 57 |
+
```
|
| 58 |
+
frame1
|
| 59 |
+
--rgb
|
| 60 |
+
-----left_distorted.png (or left.png)
|
| 61 |
+
-----right_distorted.png (or right.png)
|
| 62 |
+
--nir
|
| 63 |
+
-----left_distorted.png (or left.png)
|
| 64 |
+
-----right_distorted.png (or right.png)
|
| 65 |
+
storage.hdf5
|
| 66 |
+
```
|
| 67 |
+
The frame ids are named after their creation date.
|
| 68 |
+
**_distorted.png** image need to be undistorted. **left.png** and **right.png** are undistorted version.
|
| 69 |
+
|
| 70 |
+
**storage.hdf5** is H5 database. it contains **frame** group with children of each frame ids.
|
| 71 |
+
|
| 72 |
+
---
|
| 73 |
+
|
| 74 |
+
## 📷 Imaging System
|
| 75 |
+
|
| 76 |
+
Our robotic platform integrates:
|
| 77 |
+
|
| 78 |
+
- **Two RGB-NIR stereo cameras** (pixel-aligned RGB and NIR sensors)
|
| 79 |
+
- **LiDAR sensor**
|
| 80 |
+
- **Omnidirectional mobile base** (360° movement)
|
| 81 |
+
- **High-capacity battery** (up to 6 hours)
|
| 82 |
+
- **NIR LED bar light source** for consistent active illumination
|
| 83 |
+
|
| 84 |
+

|
| 85 |
+
|
| 86 |
+
---
|
| 87 |
+
|
| 88 |
+
## 🔧 Methods
|
| 89 |
+
|
| 90 |
+
### RGB-NIR synthetic data augmentation
|
| 91 |
+
|
| 92 |
+

|
| 93 |
+
|
| 94 |
+
See **visualize/synth_aug_render.ipynb** for method of synthetic data augmentation to build RGB-NIR training dataset.
|
| 95 |
+
|
| 96 |
+
|
| 97 |
+
### RGB-NIR Image Fusion
|
| 98 |
+

|
| 99 |
+
|
| 100 |
+
We introduce an RGB-NIR **image-level fusion technique** for 3-channel vision tasks. This approach allows existing **RGB-pretrained models** to benefit from NIR information **without additional fine-tuning**.
|
| 101 |
+
|
| 102 |
+
Applicable to:
|
| 103 |
+
- Stereo Depth Estimation
|
| 104 |
+
- Semantic Segmentation
|
| 105 |
+
- Object Detection
|
| 106 |
+
|
| 107 |
+
See **net/image_fusion.py** for pytorch implementation.
|
| 108 |
+
|
| 109 |
+
### RGB-NIR Feature Fusion (Stereo Depth)
|
| 110 |
+
|
| 111 |
+
We extend RAFT-Stereo with a novel **feature-level fusion strategy**, alternating between fused and NIR **correlation volumes** during iterative disparity estimation using GRUs.
|
| 112 |
+
|
| 113 |
+

|
| 114 |
+
|
| 115 |
+
See **net/feature_fusion.py** of implementation with RAFT-Stereo as baseline
|
| 116 |
+
Our setup reflects the **RGB with active illumination** scenario:
|
| 117 |
+
- NIR provides robust depth cues
|
| 118 |
+
- RGB complements NIR with texture under normal lighting
|
| 119 |
+
|
| 120 |
+
---
|
| 121 |
+
|
| 122 |
+
## 📊 Experimental Results
|
| 123 |
+
|
| 124 |
+
Our experiments demonstrate that pixel-aligned RGB-NIR inputs:
|
| 125 |
+
- Improve stereo depth accuracy under low-light and high-contrast conditions
|
| 126 |
+
- Enable pretrained RGB models to generalize better
|
| 127 |
+
- Enhance robustness across lighting domains
|
| 128 |
+
|
| 129 |
+
|
| 130 |
+
|
| 131 |
+
|
| 132 |
+
---
|
| 133 |
+
|
| 134 |
+
|
| 135 |
+
|
| 136 |
+
|
| 137 |
+
|
| 138 |
+
## 📄 Citation
|
| 139 |
+
|
| 140 |
+
If you use this dataset or code, please cite our work:
|
| 141 |
+
|
| 142 |
+
```bibtex
|
| 143 |
+
@article{kim2025pixelnir,
|
| 144 |
+
author = {Jinnyeong Kim and Seung-Hwan Baek},
|
| 145 |
+
title = {Pixel-aligned RGB-NIR Stereo Imaging and Dataset for Robot Vision},
|
| 146 |
+
conference = {The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
|
| 147 |
+
year = {2025},
|
| 148 |
+
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2411.18025},
|
| 149 |
+
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.18025},
|
| 150 |
+
}
|